Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsumura, Daiju; Kimura, Yusaku*; Tsuji, Takuya; Mizuki, Junichiro*
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 11(5), p.296 - 299, 2023/11
no abstracts in English
 ion complex; Presence of a Rh
ion complex; Presence of a Rh Intermediate in Direct Photoreduction
Intermediate in Direct PhotoreductionSaeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Yomogida, Takumi; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 126(12), p.5607 - 5616, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.66(Chemistry, Physical)The reaction mechanism of the direct photoreduction of a Rh ion complex to a Rh
ion complex to a Rh species induced by pulsed ultraviolet laser irradiation was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS) spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points and suggested that more than two Rh
species induced by pulsed ultraviolet laser irradiation was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS) spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points and suggested that more than two Rh species contribute toward the direct photoreduction of Rh
species contribute toward the direct photoreduction of Rh . Analysis of the time-resolved XANES data by singular value deposition showed that the direct photoreduction involves three Rh
. Analysis of the time-resolved XANES data by singular value deposition showed that the direct photoreduction involves three Rh species. Multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares analysis (MCR-ALS) of the time-resolved XANES data gave pure spectra and concentration profiles of the three Rh
species. Multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares analysis (MCR-ALS) of the time-resolved XANES data gave pure spectra and concentration profiles of the three Rh species. The Rh
species. The Rh species were assigned to Rh
species were assigned to Rh , Rh
, Rh , and Rh
, and Rh species based on the features of the pure XANES spectra. The concentration profiles suggested that the direct photoreduction proceeds in the order of Rh
species based on the features of the pure XANES spectra. The concentration profiles suggested that the direct photoreduction proceeds in the order of Rh
 Rh
Rh
 Rh
Rh . A reaction mechanism, which was proposed involving photoreductions of Rh
. A reaction mechanism, which was proposed involving photoreductions of Rh and Rh
and Rh , photoinduced autocatalytic reductions of Rh
, photoinduced autocatalytic reductions of Rh and Rh
and Rh , and photooxidation of Rh
, and photooxidation of Rh , well reproduced the concentration profiles of three Rh
, well reproduced the concentration profiles of three Rh species.
species.
Nagai, Takayuki; Sasage, Kenichi; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Ota, Toshiaki*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*; Takahashi, Tomoe*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-003, 94 Pages, 2019/09
The local structures of glass-forming elements and waste elements would change by the chemical composition of waste glass including those elements. In this study, simulated waste glass samples were prepared from borosilicate glass frit including phosphorus (P) or vanadium (V), and we investigated local structures of boron, sodium, and waste elements in these P glass and V glass samples by using synchrotron XAFS measurements in soft and hard X ray region.
Narita, Hirokazu*; Nicolson, R. M.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Ito, Fumiyuki*; Morisaku, Kazuko*; Goto, Midori*; Tanaka, Mikiya*; Heller, W. T.*; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 58(13), p.8720 - 8734, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:69.69(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Nagai, Takayuki; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Sasage, Kenichi
Busshitsu, Debaisu Ryoiki Kyodo Kenkyu Kyoten Kenkyu Seika Hokokusho (Heisei-28-Nendo) (CD-ROM), 1 Pages, 2017/03
no abstracts in English
 )
)
Lang, R.*; Li, T.*; Matsumura, Daiju; Miao, S.*; Ren, Y.*; Cui, Y.-T.*; Tan, Y.*; Qiao, B.*; Li, L.*; Wang, A.*; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 55(52), p.16054 - 16058, 2016/12
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Nagata, Hiroshi; Endo, Yasuichi; Matsui, Yoshinori; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
KAERI/GP-418/2015, p.110 - 112, 2015/00
 irradiation experiments with a
irradiation experiments with a  Co source were carried out for developing Self-Powered Gamma Detectors (SPGDs) with lead (Pb) emitter and Self-Powered Neutron Detectors (SPNDs) with Pt-40%Rh emitter prior to in-core irradiation experiments. The results showed the output currents of the SPGDs were proportional to the
Co source were carried out for developing Self-Powered Gamma Detectors (SPGDs) with lead (Pb) emitter and Self-Powered Neutron Detectors (SPNDs) with Pt-40%Rh emitter prior to in-core irradiation experiments. The results showed the output currents of the SPGDs were proportional to the  dose rate in the range from about 200-6000 Gy/h with about 10% accuracy. In the case of SPNDs, the output currents flowed in inverse direction and were an order of magnitude lower compared with that of the SPGDs. These different behaviors of the output currents are considered to be caused by the difference in the emitter sizes and the current component originated at the MI cables.
dose rate in the range from about 200-6000 Gy/h with about 10% accuracy. In the case of SPNDs, the output currents flowed in inverse direction and were an order of magnitude lower compared with that of the SPGDs. These different behaviors of the output currents are considered to be caused by the difference in the emitter sizes and the current component originated at the MI cables.

Bando, Kyoko*; Saito, Takeru; Sato, Koichi*; Tanaka, Tomoaki*; Dumeignil, F.*; Imamura, Motoyasu*; Matsubayashi, Nobuyuki*; Shimada, Hiromichi*
Topics in Catalysis, 18(1-2), p.59 - 65, 2002/01
no abstracts in English
; Kubota, Masumitsu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 30(7), p.717 - 719, 1993/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:82.84(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 -diketonates by supercritical fluid chromatography
-diketonates by supercritical fluid chromatographyK.E.Laintz*; Meguro, Yoshihiro; ; Tachikawa, Enzo
J. High Resolut. Chromatogr., 16, p.372 - 375, 1993/06
no abstracts in English
; Kawamura, Kazuhiro; Takahashi, Takeshi
PNC TN8410 91-247, 29 Pages, 1991/12
The effects of noble metal elements such as ruthenium, rhodium and palladium on the viscosity and electrical resistivity of simulated nuclear waste glass were studied. The glass enriched with noble metals showed the viscosity of a non-Newtonian fluid. The viscosity of the waste g1ass with 10 wt% RuO was 3 to 7 times higher than that of glass without noble metals. The RuO
was 3 to 7 times higher than that of glass without noble metals. The RuO was mainly responsible for the increase in viscosity for the glass enriched with noble metals. Electrical resistivity of the glass with 15 wt% RuO
was mainly responsible for the increase in viscosity for the glass enriched with noble metals. Electrical resistivity of the glass with 15 wt% RuO , was one seventh to two orders of magnitude lower than that of glass without noble metals. The three noble metals contributed to the decrease in resistivity. The quantitative effects of noble metals on these properties were obtained.
, was one seventh to two orders of magnitude lower than that of glass without noble metals. The three noble metals contributed to the decrease in resistivity. The quantitative effects of noble metals on these properties were obtained.
; Takahashi, Takeshi
PNC TN8410 91-158, 19 Pages, 1991/04
Joule heated ceramic melter has been developed to vitrify high-level liquid wastes (HLLW) from reprocessing nuclear spent fuel at Power Reacter and Nuclear Fuel Development Corporation (PNC). Noble metal elements such as ruthenium, paladium and rhodium are contained as fission products in the HLLW. The operational chracteristics of Joule-heated ceramic melter were studied on the effects of these elements. Two small scale melters with sloped floor were fabricated and tested. The slope was 30 and 45
and 45 for each. The operational characteristics including electrode resistance, temperature profile etc. were monitored. The drain efficiency of noble metal elements from the melters during the glass drain operation were evaluated. After the test operation, the melters were cut after cooled with the glass left in the melting cavities, following the termination of the test operations. The sediments of the precipitations of the noble metal elements were evaluated from the sectional observation for the melter. The results from the studies were compared between 30
for each. The operational characteristics including electrode resistance, temperature profile etc. were monitored. The drain efficiency of noble metal elements from the melters during the glass drain operation were evaluated. After the test operation, the melters were cut after cooled with the glass left in the melting cavities, following the termination of the test operations. The sediments of the precipitations of the noble metal elements were evaluated from the sectional observation for the melter. The results from the studies were compared between 30 and 45
and 45 slopes and discussed. It was concluded that the 45
slopes and discussed. It was concluded that the 45 sloped floor was clearly effective to drain the noble metal elements and the structure of the 45
sloped floor was clearly effective to drain the noble metal elements and the structure of the 45 sloped floor melter was compatible with some amount of precipitates at the bottom.
sloped floor melter was compatible with some amount of precipitates at the bottom.
; *;
Bunseki Kagaku, 18(2), p.136 - 143, 1969/00
no abstracts in English
Morita, Misaki*; Araki, Yuta*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fukutani, Satoshi*; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagai, Takayuki; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 ion complexes; Extraction of intermediates information by multivariate spectral analysis
ion complexes; Extraction of intermediates information by multivariate spectral analysisSaeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Yomogida, Takumi; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
no journal, ,
The precious metal (PM) ions complexed with negative ions and water molecules in solution has a charge transfer absorption band in the UV region. When alcohol is added to such a PM complex solution and irradiated with an ultraviolet laser, the PM
complex solution and irradiated with an ultraviolet laser, the PM complex is electronically excited and reacts with the alcohol to be reduced to the neutral atom PM
complex is electronically excited and reacts with the alcohol to be reduced to the neutral atom PM . The reduced PM
. The reduced PM spontaneously aggregates in the solution to form fine particles. This process is called Laser-Induced Particle Formation (LIPF), and is used for the formation of precious metal nanoparticles and the recovery of precious metals from factory effluents. We have investigated the LIPF reaction mechanism of Rh
spontaneously aggregates in the solution to form fine particles. This process is called Laser-Induced Particle Formation (LIPF), and is used for the formation of precious metal nanoparticles and the recovery of precious metals from factory effluents. We have investigated the LIPF reaction mechanism of Rh ion complexes by in situ energy-dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy(XAFS). As a result of analyzing the obtained XAFS spectra, we found that Rh species with three oxidation numbers are involved in the Rh
ion complexes by in situ energy-dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy(XAFS). As a result of analyzing the obtained XAFS spectra, we found that Rh species with three oxidation numbers are involved in the Rh reduction reaction, which proceeds from Rh
reduction reaction, which proceeds from Rh to Rh
to Rh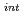 (intermediate) to Rh
(intermediate) to Rh .
.
 ion complex in a H
ion complex in a H O/EtOH solution
O/EtOH solutionSaeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Yomogida, Takumi; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
no journal, ,
The reaction mechanism of the direct photo-reduction of a Rh ion complex to a Rh
ion complex to a Rh species was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points. It suggested that more than two Rhn+ species contribute toward the reaction. We applied singular value deposition to the time-resolved XANES data and showed the contribution of three Rh
species was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points. It suggested that more than two Rhn+ species contribute toward the reaction. We applied singular value deposition to the time-resolved XANES data and showed the contribution of three Rh species to the direct photoreduction. Next, in order to extract spectral information on the Rh
species to the direct photoreduction. Next, in order to extract spectral information on the Rh intermediate, we analyzed the time-resolved XANES data using multivariate curve resolution analysis, which gives pure spectra and concentration profile of the Rh
intermediate, we analyzed the time-resolved XANES data using multivariate curve resolution analysis, which gives pure spectra and concentration profile of the Rh species. Finally, based on feature of the pure spectrum, we assigned the Rh
species. Finally, based on feature of the pure spectrum, we assigned the Rh intermediate to the Rh
intermediate to the Rh species.
species.